--> Check if the array is sorted, if sorted then the binary tree is a BST.
A binary search tree (BST) is a node based binary tree data structure which has the following properties.
• The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
• The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
• Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
From the above properties it naturally follows that:
• Each node (item in the tree) has a distinct key.
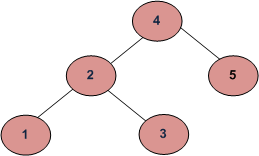
METHOD 1 (Simple but Wrong)
Following is a simple program. For each node, check if left node of it is smaller than the node and right node of it is greater than the node.
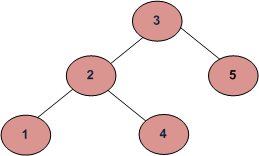
This approach is wrong as this will return true for below binary tree (and below tree is not a BST because 4 is in left subtree of 3)
METHOD 2 (Correct but not efficient)
For each node, check if max value in left subtree is smaller than the node and min value in right subtree greater than the node.
METHOD 3 (Correct and Efficient)
Method 2 above runs slowly since it traverses over some parts of the tree many times. A better solution looks at each node only once. The trick is to write a utility helper function isBSTUtil(struct node* node, int min, int max) that traverses down the tree keeping track of the narrowing min and max allowed values as it goes, looking at each node only once. The initial values for min and max should be INT_MIN and INT_MAX — they narrow from there.
/* Returns true if the given tree is a binary search tree
(efficient version). */
int isBST(struct node* node)
{
return(isBSTUtil(node, INT_MIN, INT_MAX));
}
/* Returns true if the given tree is a BST and its
values are >= min and <= max. */
int isBSTUtil(struct node* node, int min, int max)
♥ ¸¸.•*¨*•♫♪♪♫•*¨*•.¸¸♥
http://www.glassdoor.com/Interview/Test-if-a-Binary-tree-is-BST-or-not-QTN_129120.htm
http://geeksforgeeks.org/?p=3042http://www.glassdoor.com/Interview/Test-if-a-Binary-tree-is-BST-or-not-QTN_129120.htm
No comments:
Post a Comment